Overview:
Patella luxation, also known as dislocated kneecap, is a common orthopedic issue in dogs where the patella (kneecap) moves out of its normal position. This condition can affect one or both knees and is most frequently seen in small and toy breeds but can occur in dogs of any size.
Causes:
Patella luxation can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Genetic Predisposition: Some breeds are more prone to patella luxation due to inherited structural abnormalities.
- Trauma: Injury or trauma to the knee can result in the dislocation of the patella.
- Congenital Abnormalities: Some dogs are born with anatomical issues that predispose them to patella luxation.
Symptoms:
Dogs with patella luxation may exhibit one or more of the following symptoms:
- Intermittent Lameness: The affected dog may occasionally limp or hold the leg up.
- Difficulty Walking: The dog may show discomfort or difficulty in walking or climbing stairs.
- Knee Buckling: The knee may appear to buckle or snap out of place during movement.
- Abnormal Gait: A noticeable change in the way the dog walks, often with a “skipping” motion.
Diagnosis:
A thorough physical examination by a veterinarian is crucial for diagnosing patella luxation. Diagnostic tools may include:
- Physical Examination: Assessment of the knee’s range of motion and palpation to identify luxation.
- X-rays: Imaging may be used to evaluate the extent of the dislocation and rule out other potential issues.
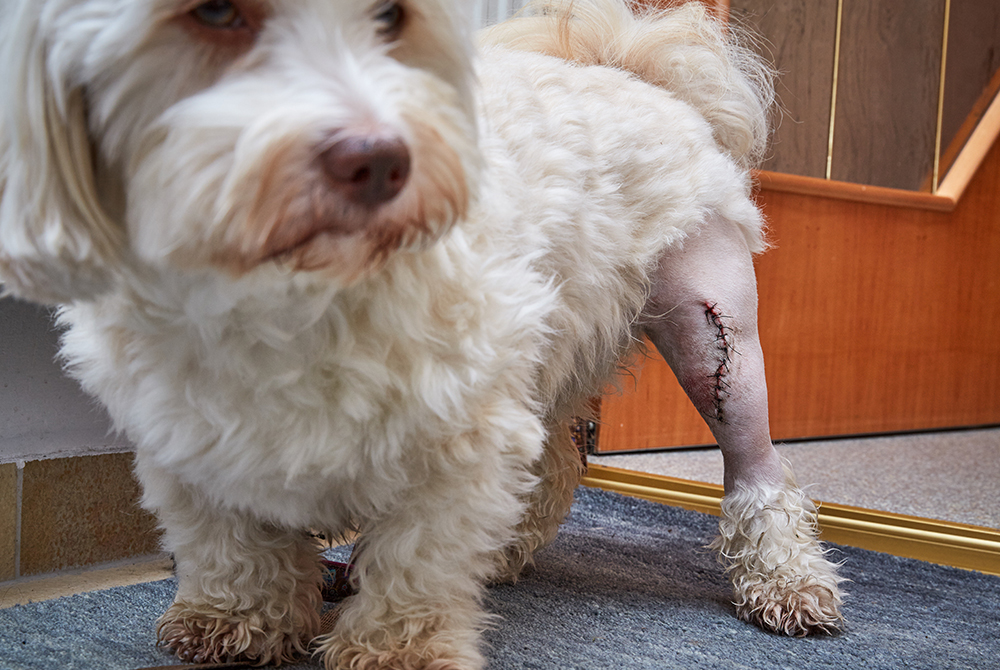
Treatment:
Treatment for patella luxation depends on the severity of the condition and the impact on the dog’s quality of life. Options may include:
- Conservative Management: For mild cases, treatment may involve rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy.
- Surgical Intervention: In more severe cases, surgery may be recommended to realign the patella and correct any underlying anatomical issues.
Prevention:
While genetic factors cannot be controlled, maintaining a healthy weight and ensuring regular exercise can help minimize the risk of patella luxation or prevent the condition from worsening.
When to Seek Help:
If you notice symptoms of patella luxation or if your dog is experiencing discomfort or difficulty walking, seek veterinary care promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve the prognosis and quality of life for your pet.
Contact Us:
If you have concerns about your dog’s health or need immediate assistance, visit Mission Veterinary Clinic. We are located in the San Fernando Valley at 16915 San Fernando Mission Blvd, Granada Hills, CA 91344. Our urgent care facility operates on a walk-in basis and does not require appointments. For more information or to speak with a veterinarian, call us at 818-363-8143.
Mission Veterinary Clinic
- Address: 16915 San Fernando Mission Blvd, Granada Hills, CA 91344
- Phone: 818-363-8143
- Website: missionvet.com








Leave A Comment