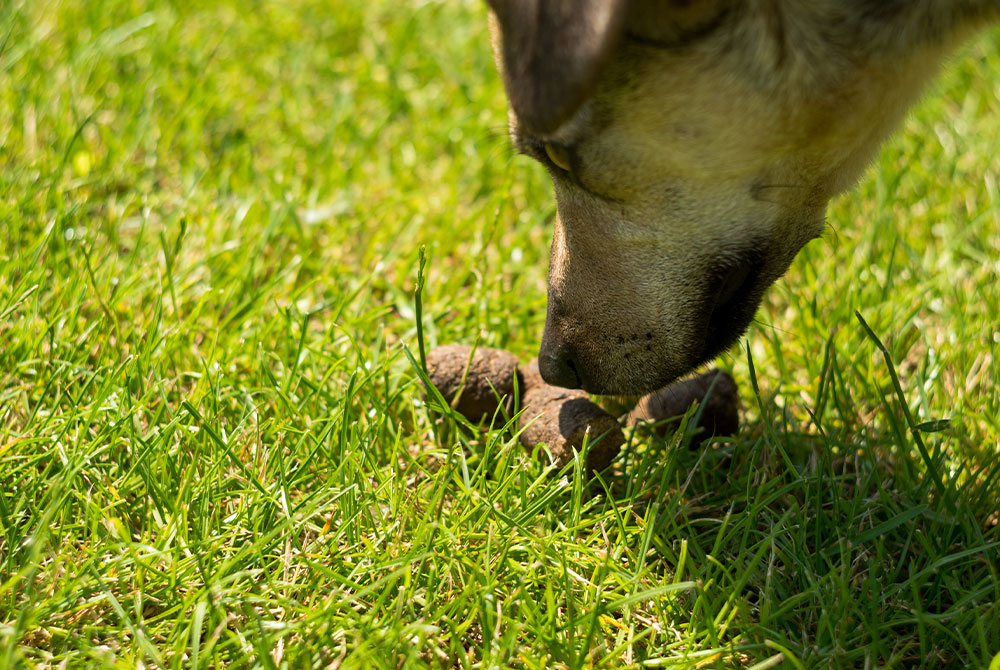
What is Coprophagia?
Coprophagia is the consumption of feces by dogs. While it may seem unusual or unpleasant to us, it is relatively common among dogs. Understanding the reasons behind this behavior and how to address it can help ensure the health and well-being of your pet.
Causes of Coprophagia
Several factors may contribute to coprophagia in dogs, including:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Dogs may eat feces to compensate for a lack of nutrients or digestive enzymes.
- Behavioral Issues: Stress, anxiety, or boredom can lead dogs to eat feces as a coping mechanism.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as gastrointestinal disorders or parasites, may cause coprophagia.
- Instinctual Behavior: Puppies may engage in this behavior as a normal part of exploring their environment.
- Attention-Seeking: Some dogs may eat feces to get attention from their owners.
Health Risks
Consuming feces can expose dogs to various health risks, including:
- Parasites: Feces can carry parasites such as worms, which can be harmful to your dog’s health.
- Bacterial Infections: Eating feces may lead to bacterial infections and gastrointestinal upset.
- Toxic Substances: Feces can contain harmful substances or toxins that may affect your dog’s health.
Preventive Measures and Solutions
If your dog is exhibiting coprophagia, consider the following steps:
- Proper Diet: Ensure your dog is receiving a balanced diet with the necessary nutrients. Consult with your veterinarian to rule out any nutritional deficiencies.
- Regular Exercise: Engage your dog in regular physical activity to reduce boredom and stress.
- Training and Behavior Modification: Implement training techniques to discourage coprophagia. Positive reinforcement and distraction methods can be effective.
- Environmental Management: Keep your dog’s environment clean by promptly disposing of feces and monitoring their behavior.
- Veterinary Consultation: If coprophagia persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, consult your veterinarian. They can help identify any underlying medical conditions and recommend appropriate treatments.
When to Seek Veterinary Care
If your dog is frequently eating feces and showing signs of illness, such as vomiting, diarrhea, or changes in appetite, it is important to seek veterinary care. At Mission Veterinary Clinic, we are equipped to handle urgent care needs and provide the necessary evaluations and treatments.
Contact Us
For more information or to address any concerns about your dog’s health, visit us at Mission Veterinary Clinic located at:
16915 San Fernando Mission Blvd, Granada Hills, CA 91344
Phone: 818-363-8143
We are open from 9 AM to 11 PM, 7 days a week. Please note that we only see patients on a walk-in basis and do not take appointments.
For further details, visit our website at missionvet.com.
Conclusion
Addressing coprophagia requires a combination of proper care, training, and veterinary guidance. By taking these steps, you can help ensure your dog’s health and well-being.









Leave A Comment